- 签证留学 |
- 笔译 |
- 口译
- 求职 |
- 日/韩语 |
- 德语
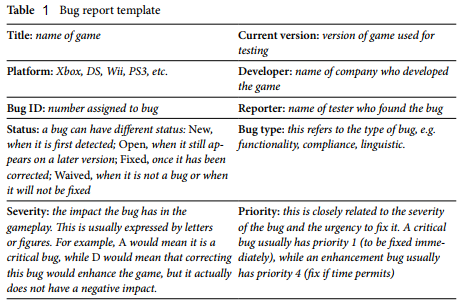
Functionality
These are the most critical type of bugs, and they are related to the game itself and its UI. Functionality bugs mainly relate to stability (e.g. does the game freeze or crash when a certain action is performed?) and game mechanics (e.g. does a particular fighting technique have the effect it is supposed to have?; Do the different commands work?) This type of testing is known as "functionality testing"
Compliance
The localized versions are checked for adherence to the technical requirements checklist, to the localization standards of each platform hardware manufacturer, and to legal, ethical, and ratings-related criteria. This type of testing is known as "compliance testing".
Linguistic errors
These are mainly bugs related to text, such as grammar mistakes, typos, truncations, overlaps, etc. This type of testing is known as "linguistic testing" Some software and game companies include cosmetic errors in this category, such as the lack of a blank space between words or the presence of extra blank spaces or extra blank lines. Other companies, however, consider them separately during the cosmetic testing. In our experience, however, most game companies have two types of testers: functionality testers and linguistic testers. Functionality testers check the game to make sure there are no technical or gameplay issues and do not necessarily speak the language of the localized versions. By comparison, linguistic testers focus on language, cosmetic, and compliance issues, such as grammar mistakes, the use of unidiomatic language, the use of incorrect platform terminology, truncations, and missing and extra spaces, although they also report any functionality bugs they detect.
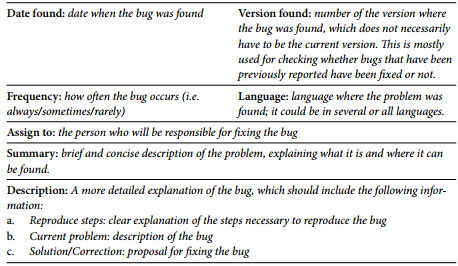
Developers and publishers design their own bug report template, although all reports tend to include similar information. When the testing progresses and the bugs are fixed, different versions are released. It is necessary to check that all reported bugs have been fixed in subsequent versions. As long as a bug has not been fixed, it is considered "open"; once it has been fixed it acquires a "closed" status and it is not necessary to check it again in subsequent versions. In addition to the three types of bug mentioned above which are widely recognised and used by the game localization industry, Edwards (2012, 21) recommends introducing a new bug category - "cultural bug - in order to ensure that any culture-related issues that may have been overlooked during the localization process are also tracked and amended as necessary, although this is not common at present. The template shown in Table 1 illustrates the most common fields found in a bug report and includes a brief explanation of them.
Once the game has been tested and the final version is nearly ready, publishers usually submit a copy of a near final version of the game, together with the appropriate documentation, to the appropriate software ratings board to obtain an age rating.
责任编辑:admin
