- 签证留学 |
- 笔译 |
- 口译
- 求职 |
- 日/韩语 |
- 德语
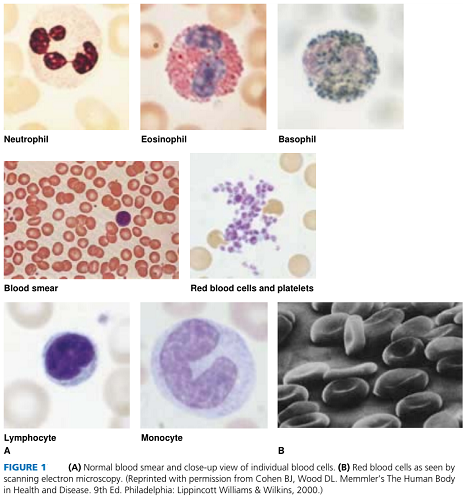
The blood cells (Fig. 1) are erythrocytes, or red blood cells; leukocytes, or white blood cells; and platelets, also called thrombocytes. All blood cells are produced in red bone marrow. Some white blood cells multiply in lymphoid tissue as well.
Erythrocytes
The major function of erythrocytes is to carry oxygen to cells. This oxygen is bound to an iron-containing pigment within the cells called hemoglobin. Erythrocytes are small, disk-shaped cells with no nucleus. Their concentration of about 5 million per µL (cubic millimeter) of blood makes them by far the most numerous of the blood cells. The hemoglobin that they carry averages 15 g per deciliter (100 mL) of blood. A red blood cell gradually wears out and dies in about 120 days, so these cells must be constantly replaced. Production of red cells in the bone marrow is regulated by the hormone erythropoietin (EPO), which is made in the kidneys.
Leukocytes
White blood cells all show prominent nuclei when stained. They total about 5,000 to 10,000 per µL, but their number may increase during infection. There are five different types of leukocytes, which are identified by the size and appearance of the nucleus and by their staining properties. Granular leukocytes or granulocytes have visible granules in the cytoplasm when stained; there are three types of granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils, named for the kind of stain they take up. Agranulocytes do not have visible granules when stained. There are two types of agranulocytes: lymphocytes and monocytes. Characteristics of the different types of white cells are given in Display Fig. 1. White blood cells protect against foreign substances. Some engulf foreign material by the process of phagocytosis; others function as part of the immune system. In diagnosis it is important to know not only the total number of leukocytes but also the relative number of each type because these numbers can change in different disease conditions. The most numerous white blood cells, neutrophils, are called polymorphs because of their various-shaped nuclei. They are also referred to as segs, polys, or PMNs (polymorphonuclear leukocytes). A band cell, also called a stab or staff cell, is an immature neutrophil with a solid curved nucleus. Large numbers of band cells in the blood indicate an active infection.
Platelets
The blood platelets (thrombocytes) are fragments of larger cells formed in the bone marrow. They number from 200,000 to 400,000 per µL of blood. Platelets are important in hemostasis, the prevention of blood loss, a component of which is the process of blood clotting, also known as coagulation.
When a vessel is injured, platelets stick together to form a plug at the site. Substances released from the platelets and from damaged tissue then interact with clotting factors in the plasma to produce a wound-sealing clot. Clotting factors are inactive in the blood until an injury occurs. To protect against unwanted clot formation, 12 different factors must interact before blood coagulates. The final reaction is the conversion of fibrinogen to threads of fibrin that trap blood cells and plasma to produce the clot. What remains of the plasma after blood coagulates is serum.
责任编辑:admin
