- 签证留学 |
- 笔译 |
- 口译
- 求职 |
- 日/韩语 |
- 德语
Coronary artery disease (CAD), which results from atherosclerosis of the vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle, is a leading cause of death in industrialized countries (see Fig.1). An early sign of CAD is the type of chest pain known as angina pectoris. This is a feeling of constriction around the heart or pain that may radiate to the left arm or shoulder, usually brought on by exertion. Often there is anxiety, diaphoresis (profuse sweating), and dyspnea (difficulty in breathing).
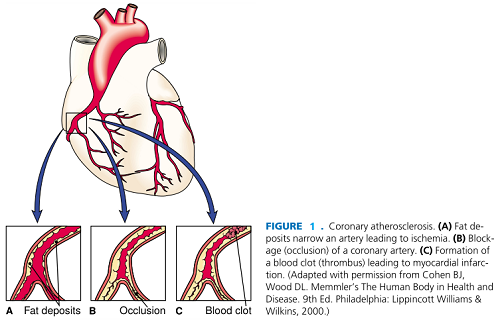
CAD is treated by control of exercise and administration of nitroglycerin to dilate coronary vessels. Other drugs may be used to regulate the heartbeat, strengthen the force of heart contraction, or prevent formation of blood clots. Patients with severe cases of CAD may be candidates for angioplasty, surgical dilatation of the blocked vessel by means of a catheter, technically called percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. If further intervention is required, the blocked vessel may be surgically bypassed with a vascular graft. In this procedure, known as a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), another vessel or a piece of another vessel, usually the saphenous vein of the leg or the left internal mammary artery, is used to carry blood from the aorta to a point past the obstruction in a coronary vessel. CAD is diagnosed by electrocardiography (ECG), study of the electrical impulses given off by the heart as it functions, stress tests, coronary angiography (imaging), echocardiography, and other tests.
Degenerative changes in the arteries predispose a person to thrombosis and sudden occlusion (obstruction) of a coronary artery. The resultant area of myocardial necrosis is termed an infarct, and the process is known as myocardial infarction (MI), the "heart attack" that may cause sudden death. Symptoms of MI include pain over the heart (precordial pain) or upper part of the abdomen (epigastric pain) that may extend to the jaw or arms, pallor (paleness), diaphoresis, nausea, and dyspnea. There may be a burning sensation similar to indigestion or heartburn.
MI is diagnosed by electrocardiography, by measurement of certain enzymes (CK, LDH, AST) released into the blood from the damaged heart muscle and by a variety of other methods. Patient outcome is based on the degree of damage and early treatment to dissolve the clot and re-establish normal heart rhythm.
责任编辑:admin
