Cholelithiasis refers to the presence of stones in the gallbladder or bile ducts, which is usually associated with cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder. Most of these stones are composed of cholesterol, an ingredient of bile. Gallstones form more commonly in women than in men, especially in women on oral contraceptives and in those who have had several pregnancies. The condition is characterized by biliary colic (pain) in the right upper quadrant (RUQ), nausea, and vomiting. Drugs may be used to dissolve gallstones, but often the cure is removal of the gallbladder in a cholecystectomy. This procedure was originally performed through a major abdominal incision, but now the gallbladder is almost always removed laparoscopically through a small incision in the abdomen.
Ultrasonography and radiography are used for diagnosis of gallstones. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) (Fig. 1) is a technique for viewing the pancreatic and bile ducts and for performing certain techniques to relieve obstructions. Contrast medium is injected into the biliary system from the duodenum and radiographs are taken.
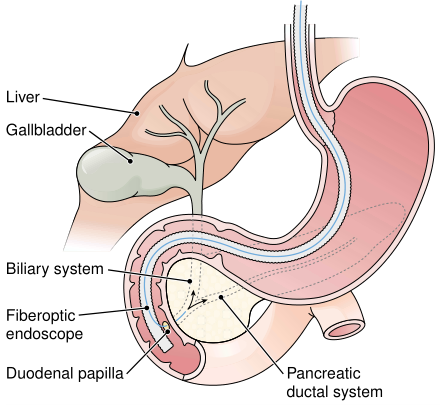
FIGURE 1. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). A contrast medium is injected into the pancreatic and bile ducts in preparation for radiography.
责任编辑:admin
上一篇:医学文章阅读——Glomerulonephritis
下一篇:医学文章阅读——Malignant Melanoma in Childhood

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。