Air is moved into and out of the lungs by the process of breathing, technically called ventilation. This consists of a steady cycle of inspiration (inhalation) and expiration (exhalation), separated by a period of rest. The cycle begins when the phrenic nerve stimulates the diaphragm to contract and flatten, thus enlarging the chest cavity. The resulting decrease in pressure within the thorax causes air to be pulled into the lungs (Fig. 1). The intercostal muscles between the ribs aid in inspiration by pulling the ribs up and out. Muscles of the neck and thorax are used in addition for forceful inhalation. The measure of how easily the lungs expand under pressure is compliance. Fluid produced within the lung, known as surfactant, aids in compliance by reducing surface tension within the alveoli. Expiration occurs as the breathing muscles relax, the lungs spring back to their original size, and air is forced out. Muscles of the rib cage and abdomen can be called on for forceful exhalation.
Breathing is normally regulated unconsciously by centers in the brainstem. These centers adjust the rate and rhythm of breathing according to changes in the composition of the blood, especially the concentration of carbon dioxide.
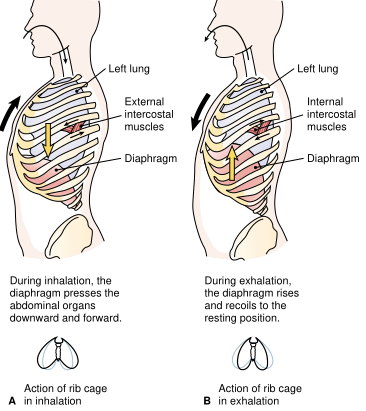
FIGURE 1. Pulmonary ventilation. (A) Inhalation. (B) Exhalation. (Reprinted with permission from Cohen BJ, Wood DL.Memmler's The Human Body in Health and Disease. 9th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000.)
责任编辑:admin
上一篇:医学文章阅读——Lung Cancer
下一篇:医学文章阅读——Myelofibrosis

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。