In general, arthritis means inflammation of a joint. The most common form is osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease (DJD) (Fig. 1). This is a gradual degeneration of articular (joint) cartilage caused by wear and tear. It usually appears at midlife and beyond and involves the weight-bearing joints and joints of the fingers. Radiographs show a narrowing of the joint cavity and thickening of the bone. The cartilage may crack and break loose, causing inflammation in the joint and exposing the underlying bone. Osteoarthritis is treated with analgesics to relieve pain, anti-inflammatory agents, such as corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and physical therapy. Predisposing factors are age, heredity, injury, congenital skeletal abnormalities, and endocrine disorders.
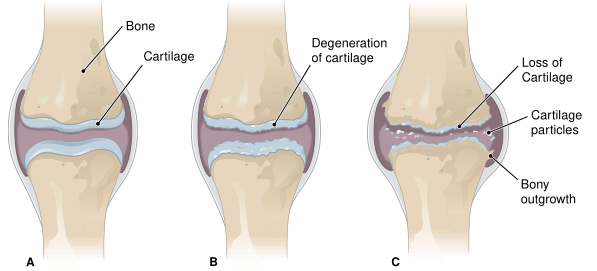
FIGURE 1. Osteoarthritis. (A) Normal joint. (B) Early stage of osteoarthritis. (C) Late stage of disease.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammatory disease of the joints that commonly appears in young adult women. Its exact causes are unknown, but it may involve immunologic reactions. A group of antibodies called rheumatoid factor often appears in the blood, but is not always specific for rheumatoid arthritis because it may occur in other systemic diseases as well. There is an overgrowth of the synovial membrane that lines the joint cavity. As this membrane covers and destroys the joint cartilage, synovial fluid accumulates, causing swelling of the joint (Fig. 2). There is degeneration of the underlying bone eventually causing fusion of the bones, or ankylosis. Treatment includes rest, physical therapy, analgesics, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
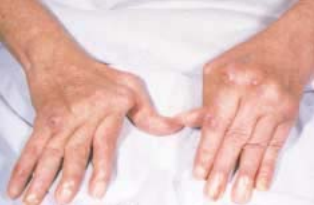
FIGURE 2. Advanced rheumatoid arthritis. The hands show swelling of the joints and deviation of the fingers. (Reprinted with permission from Rubin E, Farber JL. Pathology. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999.)
Gout is caused by an increased level of uric acid in the blood, salts of which are deposited in the joints. It mostly occurs in middle-aged men and almost always involves pain at the base of the great toe. Gout may result from a primary metabolic disturbance or may be a secondary effect of another disease, as of the kidneys. Gout is treated with drugs to suppress formation of uric acid or to increase elimination of uric acid (uricosuric agent).
责任编辑:admin
上一篇:医学文章阅读——Disorders of the Spine
下一篇:医学文章阅读——Metabolic Bone Diseases

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。