A hernia is the protrusion of an organ through an abnormal opening. The most common type is an inguinal hernia. In a hiatal hernia, part of the stomach moves upward into the chest cavity through the space (hiatus) in the diaphragm where the esophagus passes through. Often this condition produces no symptoms, but it may result in chest pain, dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing), or reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus.
In pyloric stenosis, the opening between the stomach and small intestine is too narrow. This usually occurs in infants and in male more often than in female subjects. A sign of pyloric stenosis is projectile vomiting. Surgery may be needed to correct it.
Other types of obstruction include intussusception (Fig.1), slipping of a part of the intestine into a part below it; volvulus, twisting of the intestine (see Fig.1); and ileus, intestinal obstruction often caused by lack of peristalsis. Hemorrhoids are varicose veins in the rectum associated with pain, bleeding, and, in some cases, prolapse of the rectum.
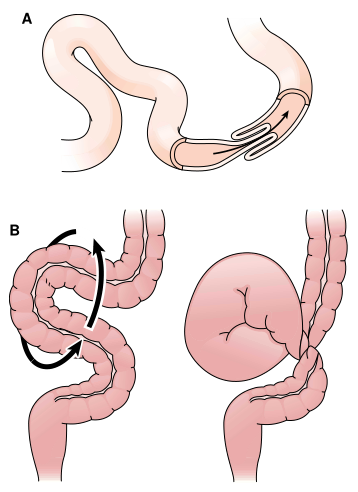
FIGURE 1. Intestinal obstruction. (A) Intussusception. (B) Volvulus, showing counterclockwise twist.
责任编辑:admin
上一篇:医学文章阅读——Ageing as Differentiation
下一篇:医学文章阅读——CANCER

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。