Leukemia is a neoplasm of white blood cells. The rapidly dividing but incompetent white cells accumulate in the tissues and crowd out the other blood cells. The symptoms of leukemia include anemia, fatigue, easy bleeding, splenomegaly, and sometimes hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver). Myelogenous leukemia originates in the bone marrow and involves mainly the granular leukocytes. Lymphocytic leukemia affects B cells and the lymphatic system, causing lymphadenopathy and adverse effects on the immune system. Leukemias are further differentiated as acute or chronic based on clinical progress. The acute forms of leukemia are acute lymphoblastic (lymphocytic) leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloblastic (myelogenous) leukemia (AML). Acute leukemia is the most common form of cancer in young children. With treatment, remission rate is high for ALL, but the prognosis in AML is poor for both children and adults. Chronic granulocytic leukemia, also called chronic myelogenous leukemia, affects young to middle-aged adults. Most cases show the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph), an inherited anomaly in which part of chromosome 22 shifts to chromosome 9. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) appears mostly in the elderly and is the most slowly growing form of the disease. The causes of leukemia are unknown but may include exposure to radiation or harmful chemicals, hereditary factors, and perhaps virus infection.
Treatment of leukemia includes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and bone marrow transplantation. One advance in transplantation is the use of umbilical cord blood to replace blood-forming cells in bone marrow. This blood is more readily available than bone marrow and does not have to match as closely to avoid rejection.
Hodgkin disease is a disease of the lymphatic system that may spread to other tissues. It begins with enlarged but painless lymph nodes in the cervical (neck) region and then progresses to other nodes. A feature of Hodgkin disease is giant cells in the lymph nodes called Reed-Sternberg cells (Fig.1). There are fever, night sweats, weight loss, and itching of the skin (pruritus). Persons of any age may be affected, but the disease predominates in young adults and those over age 50. Most cases can be cured with radiation and chemotherapy.
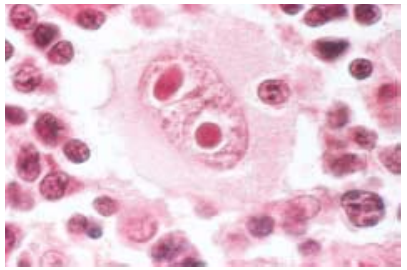
FIGURE 1. Reed-Sternberg cell typical of Hodgkin disease. (Reprinted with permission from Rubin E, Farber JL. Pathology. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999.)
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is also a malignant enlargement of lymph nodes but does not show Reed-Sternberg cells. It is more common than Hodgkin disease and has a higher mortality rate. Cases vary in severity and prognosis. It is most prevalent in the older adult population and in those with AIDS and other forms of immunodeficiency. NHL involves the T or B lymphocytes, and some cases may be related to infection with certain viruses. It requires systemic chemotherapy and, sometimes, bone marrow transplantation.
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of the blood-forming cells in bone marrow, mainly the plasma cells that produce antibodies. The disease causes anemia, bone pain, and weakening of the bones. There is a greater susceptibility to infection because of immune deficiency. Abnormally high levels of calcium and protein in the blood often lead to kidney failure. Multiple myeloma is treated with radiation and chemotherapy, but the prognosis is generally poor.
责任编辑:admin
上一篇:医学英语阅读——Definition of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Typhia
下一篇:医学文章阅读——Travelers' Diarrhea

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。