Although the various matching techniques outlined above are useful in many situations, they do have some limitations. A serious limitation of many current TM systems is their inability to deal with inflection and derivation.
Inflection is the process that is used to make a noun plural (e.g., "boy" + "s" = "boys") or to conjugate a verb (e.g., "talk" + "ed" ="talked"). In order to identify potential matches, some TM systems use very superficial methods such as comparing the overall similarity of the characters in the new and stored segments. In such cases, inflection may distort the similarity and thus prevent a potentially useful match from being retrieved, as illustrated in table 1.
Table 1. Examples of shortcomings in TM systems
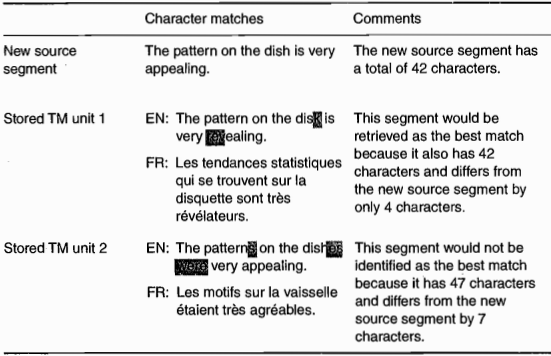
From the translator's point of view, the segment contained in TM unit 2 is actually more similar to the new source segment than is the segment contained in TM unit 1, and it would therefore be more helpful for producing an accurate translation. The differences between the new source segment and the segment in TM unit 2 are simply differences of inflection – the nouns have been pluralized and the verb has been conjugated in the past tense and made to agree with the plural subject. A translator could easily make the relevant inflectional adjustments in the new source text. In contrast, although the new source segment and the segment stored in TM unit 1 are quite similar on a superficial level (in terms of the total similarity of the individual characters), they are very different in terms of their meaning. In this case, the differences are not merely a result of inflection; rather, they are completely different lexical items that have very different translations and would therefore be of limited use in helping the translator deal with the new source-text segment.One step toward improving TM systems would be to enable them to recognize and match variants of a word (i.e., so that "dish" would match "dishes" but not "disk").
The underlying assumption here is that for a user who wishes to find translations for a sentence containing a given word X, the translations of any sentence containing an inflectional variant of X (such as Xes or Xing,) could be potentially informative, regardless of the minor adjustments that would need to be made to accommodate the inflectional variation. A similar approach could be used to deal with derivation, which is the process of adding a prefix or suffix to an existing word in order to create a new one (e.g., the addition of the suffix "ly" to the adjective "cautious" produces the adverb "cautiously").
责任编辑:admin
上一篇:规划推理算法
下一篇:理解固定模式的情境的脚本

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。