The most basic feature provided by a corpus-analysis tool is a word-frequency list, which allows users to discover how many different words are in a corpus and how often each appears. These two figures are referred to as types and tokens. For illustrative purposes, suppose that a corpus consists of the following sentence:
I really like translation because I think that translation is really, really fun.
This sentence contains a total of thirteen words; therefore, the corpus contains thirteen tokens. However, some of the words appear more than once (I, really, translation); therefore, the corpus contains only nine different words, and these are known as types. In a word-frequency list, the types are presented in a list and the number of tokens (the number of times that word occurs) is shown beside the type. This is illustrated in figure 1.
Word-frequency lists can be manipulated in a number of ways. They can be sorted in various different orders, including order of occurrence in the corpus, alphabetical order, and order of frequency, and these lists can be arranged in ascending or descending order. Therefore, the same word list can be arranged in at least six different ways, as shown in figures 2, 3, and 4.

Figure 1 A word-frequency list showing types on the left and tokens on the right.
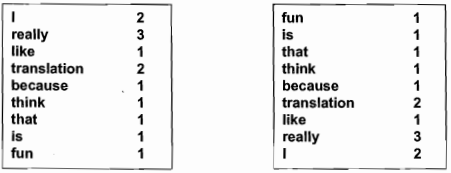
Figure 2 Word-frequency lists sorted in order of appearance in the corpus, in descending order (from the beginning of the corpus to the end) and ascending order (from the end of the corpus to the beginning).
The single-sentence corpus used in the above examples is purely for illustrative purposes – a translator would not need to use a computerized tool to analyze a single sentence. Normally, a corpus would be much larger – often in the order of hundreds of thousands or even millions of words. In such cases, the advantage of having a computer to help with counting and sorting becomes clear!
In addition to counting the frequency of words, corpus-analysis tools calculate the ratio of types to tokens. Some corpus-analysis tools can also count the number of sentences and paragraphs and calculate the average length of words, sentences, and paragraphs in the corpus.
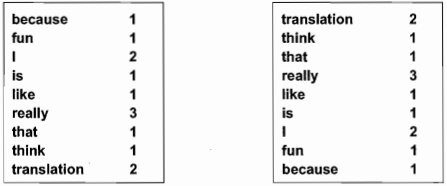
Figure 3 Word-frequency lists sorted in alphabetical order, in descending order (from A to Z) and ascending order (from Z to A).
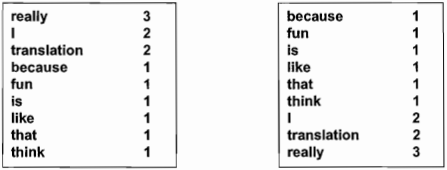
Figure 4 Word-frequency lists sorted in order of frequency, in descending order (from the most frequent to the least frequent) and ascending order (from the least frequent to the most frequent). When multiple words have the same
frequency count, they are further sorted in alphabetical order.
This type of information can help translators assess some of the stylistic features of the texts in the corpus.
责任编辑:admin
上一篇:Monolingual Concordancers
下一篇:Some Different Types of Electronic Corpora

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。