代词是代替名词的词, 按其意义、特征及其在句中的作用分为:人称代词、物主代词、指示代词、反身代词、相互代词、疑问代词、不定代词和关系代词等。
1.人称代词
1)人称代词的人称、数和格,如下表所示。
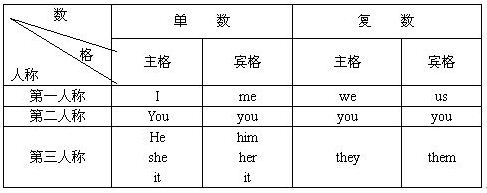
2)人称代词有主格和宾格之分。通常主格作主语,宾格作宾语。如:
I like table tennis. (作主语)
Do you know him?(作宾语)
3)人称代词还可作表语。作表语时用宾格。如:
---Whos is knocking at the door?
---It's me.
4)人称代词在than之后与其他人或事物进行比较时,用主格和宾格都可以。如:
He is older than me.
He is older than I am.
2. 物主代词
1)表示所有关系的代词叫物主代词。物主代词分形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词,如下表所示。
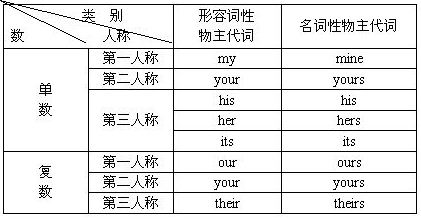
2)形容词性物主代词的作用相当于形容词,可在句中作定语。例如:
Our teacher is coming to see us.
This is her pencil-box.
3)名词性物主代词的作用相当于名词,在句中可用作主语、宾语和表语。
Our school is here, and theirs is there.(作主语)
--- Is this English-book yours? (作表语)
--- No. Mine is in my bag.
I've already finished my homework. Have you finished yours? (作宾语)
3. 指示代词
指示代词包括:this,that,these,those。
1) this和these一般用来指在时间或空间上较近的事物或人,that和those
则指时间和空间上较远的事物或人,例如:
This is a pen and that is a pencil.
We are busy these days.
In those days the workers had a hard time.
上一篇:英语介词简单介绍
下一篇:英语形容词和副词简单介绍

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。