Pleurisy, also called pleuritis, is an inflammation of the pleura, usually associated with infection. Pain is the common symptom of pleurisy. Because this pain is intensified by breathing or coughing, as the inflamed membranes move, breathing becomes rapid and shallow. Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat the symptoms of pleurisy.
As a result of injury, infection, or weakness in the pleural membrane, substances may accumulate between the layers of the pleura. When air or gas collects in this space, the condition is termed pneumothorax (Fig. 1). Compression may result in collapse of the lung, termed atelectasis.
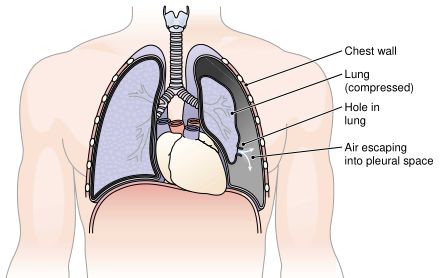
FIGURE 1. Pneumothorax. Injury to lung tissue allows air to leak into the pleural space and put pressure on the lung.
In pleural effusion, other materials accumulate in the pleural space (Fig. 2). Depending on the substances involved, these are described as empyema (pus), also termed pyothorax; hemothorax (blood); or hydrothorax (fluid). Causes of these conditions include injury, infection, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism. Thoracentesis, needle puncture of the chest to remove fluids (Fig. 2), or fusion of the pleural membranes (pleurodesis) may be required.
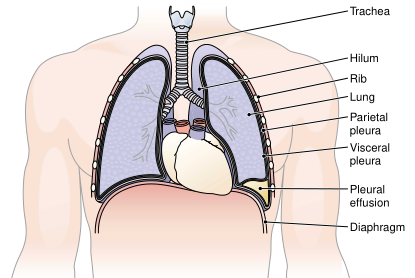
FIGURE 2. Pleural effusion. An abnormal volume of fluid collects in the pleural space.
责任编辑:admin
上一篇:中医翻译例文——病本/In Treating the Root and Branch of the Disease
下一篇:中医翻译例文——厥病/Jue-Syndrome

微信公众号搜索“译员”关注我们,每天为您推送翻译理论和技巧,外语学习及翻译招聘信息。