- 签证留学 |
- 笔译 |
- 口译
- 求职 |
- 日/韩语 |
- 德语
Genetically inherited proteins on the surface of red blood cells determine blood type. More than 20 groups of these proteins have now been identified, but the most familiar are the ABO and Rh blood groups. The ABO system includes types A, B, AB, and O. The Rh types are Rh positive (Rh+) and Rh negative (Rh−). In giving blood transfusions, it is important to use blood that is the same type as the recipient's blood or a type to which the recipient will not show an immune reaction, as described below. Compatible blood types are determined by cross-matching, as illustrated in Figure 1. Whole blood may be used to replace a large volume of blood lost, but in most cases requiring blood transfusion, a blood fraction such as packed red cells, platelets, plasma, or specific clotting factors is administered.
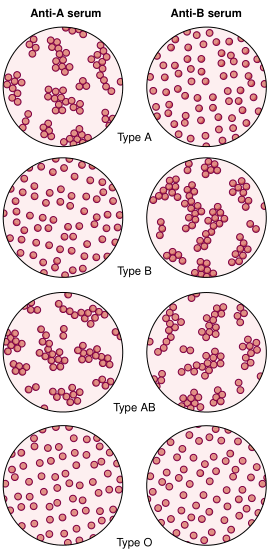
FIGURE 1. Blood typing. Red cells in type A blood are agglutinated (clumped) by anti-A serum; those in type B blood are agglutinated by anti-B serum. Type AB blood cells are agglutinated by both sera, and type O blood is not agglutinated by either serum. (Reprinted with permission from Cohen BJ, Wood DL. Memmler's The Human Body in Health and Disease. 9th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000.)
责任编辑:admin
